Open a Simulation
How to open an existing EMode simulation.
This code example is licensed under the BSD 3-Clause License.
import emodeconnection as emc
## Run an initial session with a unique simulation name.
# Set simulation parameters
wavelength = 1970 # [nm] wavelength
dx, dy = 10, 5 # [nm] resolution
trench = 1200 # [nm] waveguide side trench width
t_clad = 1200 # [nm] waveguide top/bot clad
b_clad = 1500 # [nm] waveguide top/bot clad
w_core = 1734 # [nm] waveguide core width
h_core = 150 # [nm] waveguide core height
h_slab = 20 # [nm] slab thickness in etched areas
angle = 17 # [degrees] waveguide sidewall angle
width = w_core + trench*2 # [nm] window width
height = h_core + b_clad + t_clad # [nm] window height
num_modes = 1 # [nm] number of modes
boundary = 'TE'
# Connect and initialize EMode
em = emc.EMode(simulation_name = 'GaAs_SHG')
# Settings
em.settings(
wavelength = wavelength,
x_resolution = dx, y_resolution = dy,
window_width = width, window_height = height,
boundary_condition = boundary, num_modes = num_modes,
background_material = "Air")
# Draw shapes
em.shape(name = "BOX", material = "SiO2", height = b_clad)
em.shape(name = "core", material = "GaAs", sidewall_angle = angle,
mask = w_core, height = h_core, etch_depth = h_core - h_slab)
# Launch FDM solver
em.FDM()
em.report()
em.close()
## The previous simulated can be opened again, modified, and saved with a new name.
# Open existing simulation file
em = emc.EMode(simulation_name = 'GaAs_SHG',
open_existing = True, new_name = 'GaAs_SHG-TM')
# Get the previous wavelength setting and convert it to the second harmonic wavelength
wavelength = em.get('wavelength')/2
n_eff = em.get('effective_index')
# Update the settings
em.settings(wavelength = wavelength,
boundary_condition = 'TM', num_modes = 4,
max_effective_index = n_eff[0])
# Launch FDM solver
em.FDM()
em.report()
em.close()
## When opening an existing file to only retrieve and plot data, a new simulation name is not needed since the simulation data will not be modified.
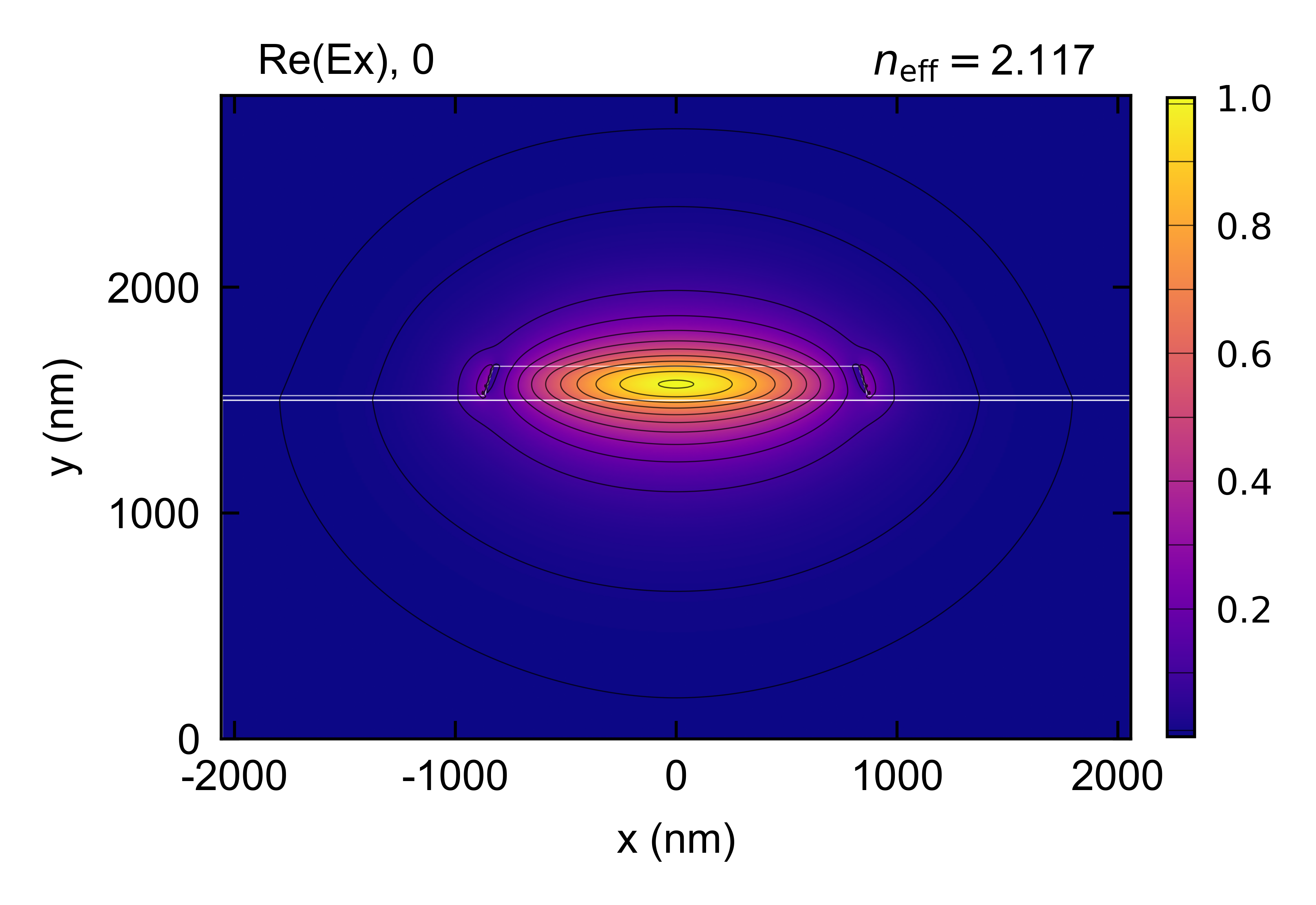
# Plot from existing simulation file - pump mode
em = emc.EMode(simulation_name = 'GaAs_SHG', open_existing = True)
E_p = em.get_fields(key = ['Ex', 'Ey', 'Ez'])
em.plot()
em.close()
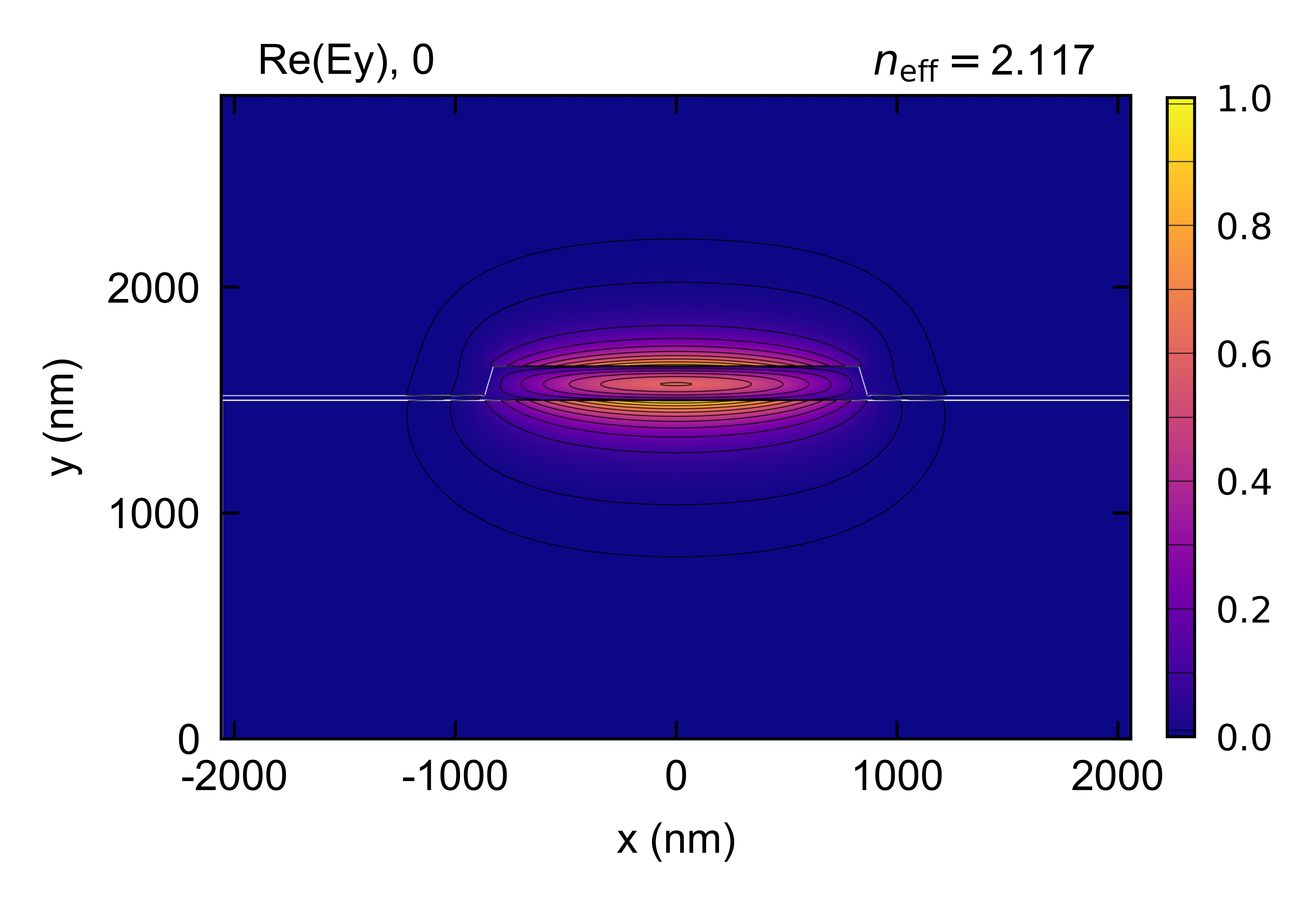
# Plot from existing simulation file - signal mode
em = emc.EMode(simulation_name = 'GaAs_SHG-TM', open_existing = True)
E_s = em.get_fields(key = ['Ex', 'Ey', 'Ez'])
TM_indices = em.get('TM_indices')
em.plot(component = 'Ey', mode = TM_indices)
em.close()
%% Run an initial session with a unique simulation name.
% Set simulation parameters
wavelength = 1970; % [nm] wavelength
dx = 10; dy = 5; % [nm] resolution
trench = 1200; % [nm] waveguide side trench width
t_clad = 1200; % [nm] waveguide top/bot clad
b_clad = 1500; % [nm] waveguide top/bot clad
w_core = 1734; % [nm] waveguide core width
h_core = 150; % [nm] waveguide core height
h_slab = 20; % [nm] slab thickness in etched areas
angle = 17; % [degrees] waveguide sidewall angle
width = w_core + trench*2; % [nm] window width
height = h_core + b_clad + t_clad; % [nm] window height
num_modes = 1; % [nm] number of modes
boundary = 'TE';
% Connect and initialize EMode
em = emodeconnection(simulation_name = 'GaAs_SHG');
% Settings
em.settings( ...
wavelength = wavelength, ...
x_resolution = dx, y_resolution = dy, ...
window_width = width, window_height = height, ...
boundary_condition = boundary, num_modes = num_modes, ...
background_material = 'Air');
% Draw shapes
em.shape(name = 'BOX', material = 'SiO2', height = b_clad);
em.shape(name = 'core', material = 'GaAs', sidewall_angle = angle, ...
mask = w_core, height = h_core, etch_depth = h_core - h_slab);
% Launch FDM solver
em.FDM();
em.report();
em.close();
%% The previous simulated can be opened again, modified, and saved with a new name.
% Open existing simulation file
em = emodeconnection(simulation_name = 'GaAs_SHG', ...
open_existing = true, new_name = 'GaAs_SHG-TM');
% Get the previous wavelength setting and convert it to the second harmonic wavelength
wavelength = em.get('wavelength')/2;
n_eff = em.get('effective_index');
% Update the settings
em.settings(wavelength = wavelength, ...
boundary_condition = 'TM', num_modes = 4, ...
max_effective_index = n_eff(1));
% Launch FDM solver
em.FDM();
em.report();
em.close();
%% When opening an existing file to only retrieve and plot data, a new simulation name is not needed since the simulation data will not be modified.
% Plot from existing simulation file - pump mode
em = emodeconnection(simulation_name = 'GaAs_SHG', open_existing = true);
E_p = em.get_fields(key = {'Ex', 'Ey', 'Ez'});
em.plot();
em.close();
% Plot from existing simulation file - signal mode
em = emodeconnection(simulation_name = 'GaAs_SHG-TM', open_existing = true);
E_s = em.get_fields(key = {'Ex', 'Ey', 'Ez'});
TM_indices = em.get('TM_indices');
em.plot('component', 'Ey', 'mode', TM_indices(1));
em.close();
Console output:
EMode 0.2.4 - email
Meshing completed in 0.5 sec
Solving modes... completed in 1.5 sec
Wavelength: 1970.0 nm
Mode # n_eff TE % Loss (dB/m)
-------- -------- ------ -------------
TE-0 2.094190 99.8 % 0.000
Exited EMode
EMode 0.2.4 - email
Meshing completed in 0.6 sec
Solving modes... completed in 1.8 sec
Wavelength: 985.0 nm
Mode # n_eff TE % Loss (dB/m)
-------- -------- ------ -------------
TE-0 2.863080 99.9 % 0.000
TE-1 2.684545 99.7 % 0.000
TE-2 2.362233 98.6 % 0.000
TM-3 2.067847 1.2 % 0.000
Exited EMode
EMode 0.2.4 - email
Exited EMode
EMode 0.2.4 - email
Exited EMode
Figures: